1-Minute Summary
- Terpene testing for cannabis enhances product differentiation and consumer satisfaction by providing insights into aroma, flavour, and effects.
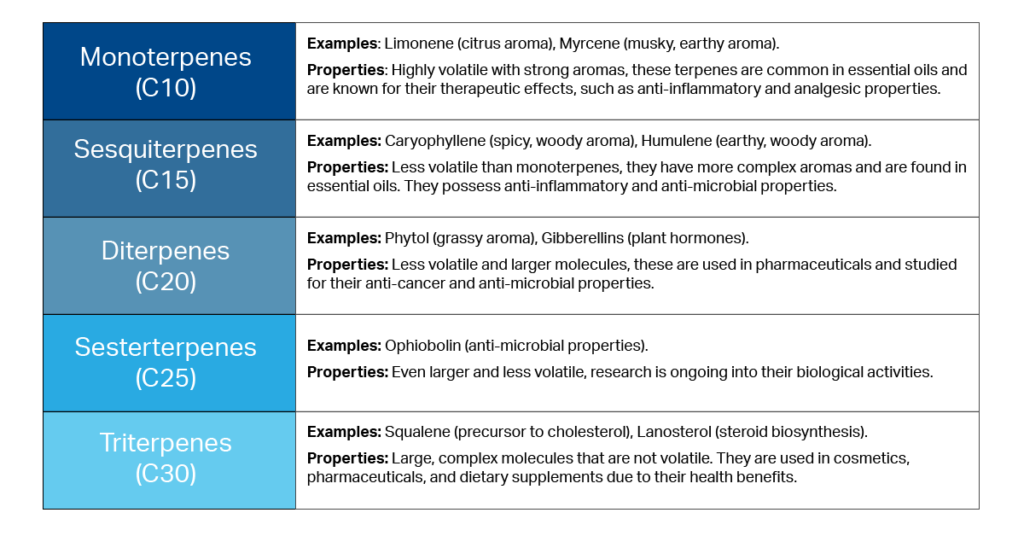
- There are five categories of cannabis terpenes: monoterpenes, sesquiterpenes, diterpenes, sesterterpenes, and triterpenes, each with unique structures and effects.
- Understanding terpenoids, esters, thiols, and phenolics is crucial for appreciating the full spectrum of plant-based compounds.
- Accurate terpene testing depends on proper sample preparation to ensure sample homogeneity through grinding or freeze-grinding.
- Specialized smoke and vapour testing reveals how terpene profiles change during consumption, providing insights into the true user experience.
Intro to Cannabis Terpenes
Terpenes are an essential component of cannabis, significantly influencing its aroma, flavour, and effects. Understanding terpenes helps consumers and researchers alike better appreciate and use cannabis.
This article delves into the science behind terpenes, their roles in cannabis, and how labs conduct cannabis terpenes testing.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are often thought of as a single, monolithic entity by some consumers, but they represent a diverse and complex class of organic compounds. This complexity is crucial to understanding the full range of their effects and applications, particularly in cannabis.
Terpenes are responsible for the distinctive scents of various plants, serving both as attractants for pollinators and deterrents for predators. However, their roles extend far beyond aroma.
In cannabis, terpenes – often attributed as having a significant contribution to the plant’s effects – enhance the overall experience through interactions with cannabinoids and other compounds.
There are five categories of terpenes, distinguished by their number of isoprene units.
Categories of Terpenes
Beyond Cannabis Terpenes: Terpenoids, Esters, Thiols, and Phenolics
While terpenes are the most well-known aromatic compounds in plants, they are just one part of a broader chemical landscape that includes terpenoids, esters, thiols, and phenolics.
These compounds each have unique structures and functions that contribute to the diverse aromas, flavours, and therapeutic properties of plants.
- Terpenoids are modified terpenes with additional functional groups, enhancing their chemical complexity and bioactivity.
- Esters are known for their sweet or fruity scents, making them essential in flavours and fragrances.
- Thiols, containing sulfur, have strong odors and significant roles in plant defense and flavour profiles.
- Phenolics, such as flavonoids, are characterized by their antioxidant properties and are crucial for plant health and human nutrition.
Understanding these differences is key to appreciating the complexity and potential of plant-based compounds.
The Role of Terpenes in Cannabis
Terpenes play a crucial role in shaping the cannabis experience. They interact with cannabinoids like THC and CBD, enhancing or modulating their effects in what is known as the “Entourage Effect”, which continues to be a topic of study.
This interaction means that two cannabis strains with the same cannabinoid profile can have different effects due to their unique terpene compositions. Thus, understanding terpenes is fundamental to both recreational and medicinal cannabis use.
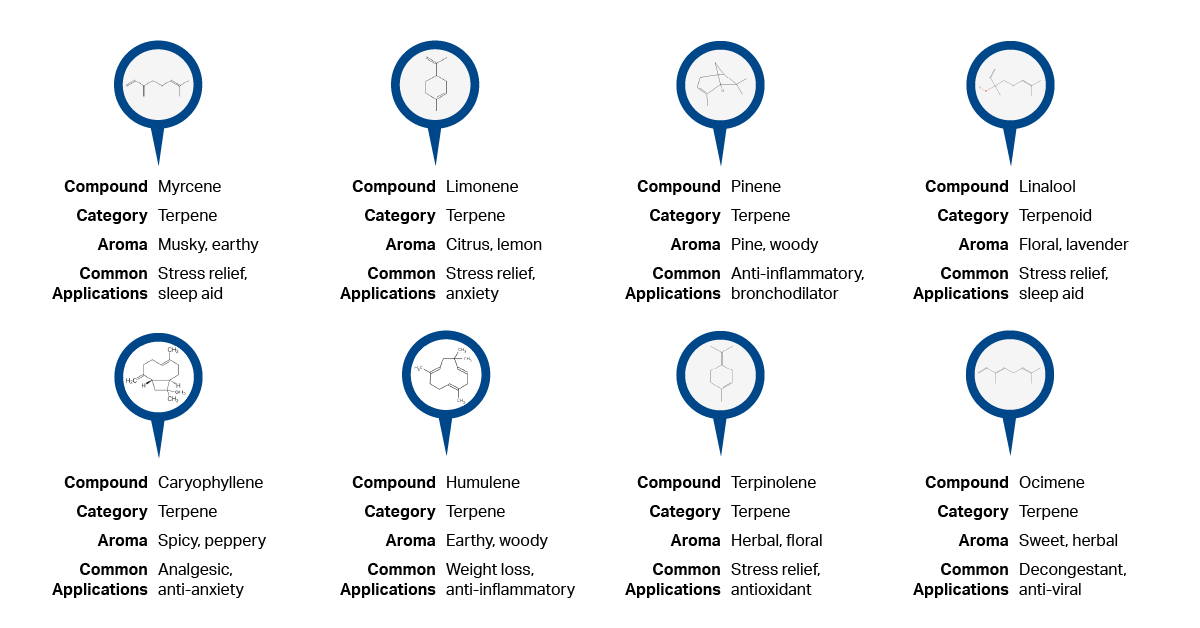
Common Cannabis Terpenes (Terpenes Chart)
Below is a cannabis terpenes chart of some of the most common terpenes found in cannabis, detailing their aromas, effects, and common applications in which they are typically found. It highlights the diversity of terpenes and their multifaceted roles in shaping the cannabis experience.
This is only a highlight of the most common cannabis terpenes; there are dozens more (for example, Labstat currently tests for 59 terpenes), and research continues to identify new terpenes and their effects on the user experience.
How Cannabis Terpene Testing is Performed
Lab testing provides detailed terpene profiling for your products, which can be used to inform product labels and marketing.
Importance of Sample Preparation
The accuracy of cannabis terpene profiling heavily relies on how the sample is prepared – an area where quality labs separate themselves.
Sample preparation for cannabis testing is a critical and often debated topic. The specific steps depend on the study’s objectives, which should be discussed with the lab during the planning phase. Proper preparation is essential, as it can significantly impact the results. The goal is to create a representative sample that accurately reflects the terpene profile.
Labstat’s scientists are available to guide you through these preparation steps to ensure accurate and reliable testing results.
Analytical Process
After the sample is prepared, it is extracted in a solvent. This extract is then filtered to remove plant particles and injected into an instrument for analysis.
A gas chromatograph with mass spectral detection separates the compounds based on molecular weight and boiling point, allowing for the accurate quantification of terpenes. Mass spectral detection also provides a secondary mechanism to confirm their identification. Typically, the smaller and more volatile molecules elute first, followed by heavier ones.
To ensure accuracy, internal standards, often isotope-labeled analogues of the compounds of interest, are added to the samples. Certified standards for each terpene help identify and quantify the terpenes present in the sample with greater certainty. The use of certified and isotope-labeled internal standards differentiates a quality lab from other labs identifying and quantitating terpenes with a limited number of surrogate standards and a non-specific detection system to save money.
Cannabis Smoke and Vapour Testing
While traditional product testing provides a snapshot of the terpene profile, it does not account for changes that occur during consumption. This is where smoke and vapour testing become essential.
Labstat, leveraging its experience in specialized emissions research, conducts comprehensive testing of cannabis smoke and vapour.
This process uses specialized equipment for the generation and collection of emissions from the smoking or vaping of cannabis products. Machine generation of emissions requires standardized conditions (e.g. puff size volume, duration, profile and frequency), where the resulting deliveries from cannabis pre-rolls, heat-not-burn, or e-vapour devices are collected for analysis. The protocol does not replicate the deliveries to an individual consumer. However, it is intended provide a common basis for a comparison of yields from products within established ranges of human smoking/vaping behaviour.
Testing these emissions reveals how terpenes transfer from the product to the emissions, offering insights into changes in flavour and chemical composition during use. The terpene profile evolves as the product is combusted or heated, influenced by factors like volatility, degradation, and by-product formation. This analysis provides valuable information for understanding the consumer experience and guiding product development.
Scientific Research on Terpenes
Recent studies have increasingly highlighted the potential therapeutic benefits of terpenes found in cannabis, emphasizing their roles in pain relief, anti-inflammatory effects, and their interactions with cannabinoids. While this is a developing area of research, we offer some examples of recent studies for your interest:
- A 2024 study conducted by researchers at the University of Arizona Health Sciences tested the pain-relieving capabilities of several terpenes found in cannabis, including alpha-humulene, beta-caryophyllene, beta-pinene, geraniol, and linalool. The study discovered that these terpenes were as effective as morphine in reducing chronic neuropathic pain, and when combined with morphine, they significantly enhanced pain relief without adverse side effects.
- Another explored the interactions between cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids. This review reinforced the concept of the Entourage Effect, where the combined action of these compounds produces a synergistic therapeutic effect greater than the sum of their individual effects. The study researchers emphasized that terpenes could modulate the pharmacokinetics and pharmacodynamics of cannabinoids, potentially enhancing their effects on the body, including analgesic, anti-inflammatory, and neuroprotective actions.
- This 2019 study highlighted the diverse medicinal properties of terpenes. Notably, monoterpenes showed promising antiviral activity, while other terpenes demonstrated potential as anti-cancer and anti-diabetic agents. Curcumin exhibits anti-inflammatory, anti-oxidant, and anti-cancer properties, gaining popularity in health foods and medical research.
The Importance of Terpenes in the Cannabis Industry
The cannabis industry isn’t all about THC – other cannabinoids and terpenes have a major effect on the product’s attributes.
Many product labels now include specific information about the terpene profile, allowing consumers to make informed choices. In this environment, you don’t want your product labels to say “terpenes may vary” lest the consumer move on to another product.
For producers, it’s vital to conduct terpene lab testing on your cannabis products and include that information on your labels. This type of product stewardship will go a long way toward ensuring satisfied, loyal customers.


