The Importance of THC in the Legal Cannabis Industry
THC is one of the most important attributes to understand about your products. Potency plays a pivotal role in product quality, regulatory considerations, and the user experience. If your product label makes a potency claim that is misaligned with your customers’ experience, it reflects poorly on your brand.
With so much focus and value put on this one molecule, accurately quantifying the THC values within legal cannabis products has never been more important.
Determining Accurate THC Values
So, how can you determine if the cannabis potency results you’re getting from your laboratory are accurate and represent the true value of THC in your products?
First, you have to know a few things about variability.
Understanding Variability in Analytical Chemistry
Variability refers to the degree to which data points in a dataset diverge from the average value and from each other.
In analytical chemistry, variability is characterized by the extent to which repeated measurements of the same test item yield differing outcomes. These differences may arise under stable conditions or due to changes in factors such as time, temperature, or operator.
This definition is multifaceted, requiring a detailed examination of how variability can influence the measured cannabinoid content in your sample.
Impact of Measurement Conditions on Variability
The first part of the definition of variability refers to the tendency of the measurement process to produce slightly different outcomes. On the surface this seems to be a straightforward statement; however, we first need to define what a measurement process is to truly understand what the definition is outlining.
A Measurement Process
A measurement process is the entire collection of procedural steps taken to execute a measurement.
In some cases, the process is simple; like when we measure the mass of a sample. This is considered a direct measurement where the entire measurement process consists of one step – placing the sample on the balance.
Complex Measurement Processes
In contrast, some measurement processes are very complex, as is the case when we measure the cannabinoid content in a sample of dried cannabis flower. This measurement process consists of five steps:
- Selecting the sample or sub-sample
- Homogenizing the sample
- Extracting the cannabinoids from the plant material
- Purification of the extract
- Analysis by HPLC
Given the complexity of this process, there is a higher tendency for it to give slightly different measurement outcomes when the analysis is repeated over time.
Achieving Consistency in Complex Processes
It’s akin to baking a loaf of bread exactly the same way day after day; even experienced bakers will tell you that achieving consistent results is one of the most difficult aspects of baking.
The freshness and temperature of the ingredients, the humidity in the room, the age of your oven, and other factors influence the rate of variability of your bread-making processes. Similarly, achieving precise and accurate results from complex measurement processes is one of the greatest challenges of analytical chemistry.
Variability and Analytical Chemistry: Conditions and Effects
The second part of the variability definition describes the conditions that can affect the results obtained, such as…
- Time
- Temperature
- Operator
When we examine variability from an analytical chemistry perspective, the spread of outcomes can be affected by each of these conditions and processes in an interdependent manner.
Establishing Variability Through Experiments
Establishing the variability of a particular analytical measurement process requires a series of deliberate and controlled experiments. These experiments are designed to identify how each factor contributes to the overall spread in the measurement outcomes. Analyzing the results of these experiments will identify a range of measurements that includes the true value.
Example: THC Potency Results and HPLC Variability
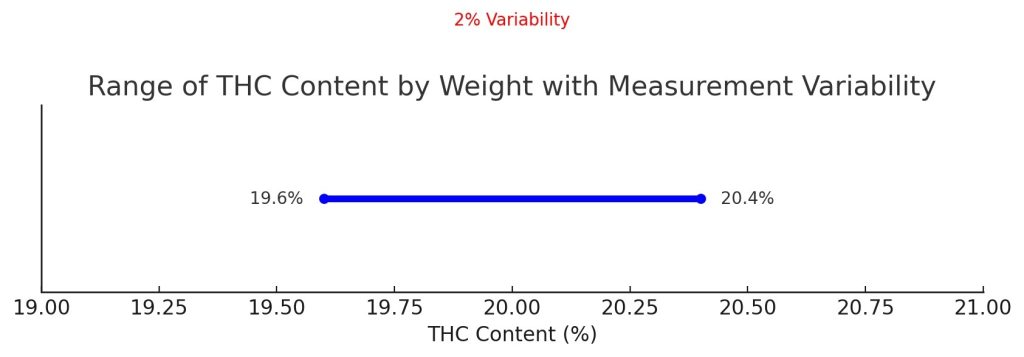
Suppose an HPLC method is used to measure the cannabinoid content in a sample of dried cannabis flower. The method has been determined to have a 2% variability, meaning the sample’s true cannabinoid content is somewhere between +/- 2% of the measured number. A value of 10 mg/g with a 2% variability may be between 10+10*2% and 10-10*2% (i.e. 9.8-10.2 mg/g).
A Practical Example
The sample submitted shows a final measured result of 20% THC content by weight. Given the HPLC method has a 2% variability as mentioned above, there is a high degree of certainty that the true THC content in the sample is a value between 19.6% and 20.4%.
From this example, you can see how the variability of a measurement process produces a result that occurs not in a single definitive point, but in a range, with the true value falling somewhere inside that range.
How THC is Reported on Your COA
Due to measurement uncertainty and the challenges of measuring the concentration of any compound, THC potency results are given from the lab as a range. For example, THCA might be reported on a Certificate of Analysis from different labs as…
- Lab A: 23% +/- 5%
- Lab B: 25% +/- 3%
So, which is correct? They may both be correct!
The actual THCA concentration of that particular sample might be 22%, which falls within the range given by both labs. If you’re the grower, you surely prefer the results from Lab B, and that’s what you want on your label. However, if another lab tests the same sample, they may report a lower potency number…and still be correct.
Reporting potency as a single number rather than a range creates misunderstandings. As we discussed in this Stratcann article, the industry could take a step toward solving the “potency inflation” problem by agreeing to report potency within, for example, a 6-point or 8-point range.
Reporting Variability in Analytical Laboratories
This poses an important question: why don’t analytical laboratories report this range rather than the exact number measured?
Generally, it is presumed that laboratories don’t report the full range as variability. Determining whether or not a product meets quality standards will be based on a set of specifications predetermined by the manufacturer.
For instance, if you expect your sample to test at 20% THC and the lab reports the measured value as 19.8%, then the sample is considered to be within the range of acceptance.
Choosing the Right Laboratory
That’s why knowing the variability of the methods used by your cannabis testing laboratory is key to understanding whether a product meets your quality expectations. Choose a lab that has verified and validated test methods and can provide details on the variability for each process they use. They should be more than willing to share this information with you and explain how they conducted their experiments and interpreted the results.
Understanding THC Testing for Accurate Product Representation
When you understand the measurement process used to test your products, you’ll have more confidence in the accuracy and specificity of the results reported on your Certificate of Analysis and thus the information you’re providing to your partners and end consumers.
Contact Labstat if you need potency testing or other cannabis testing services.



